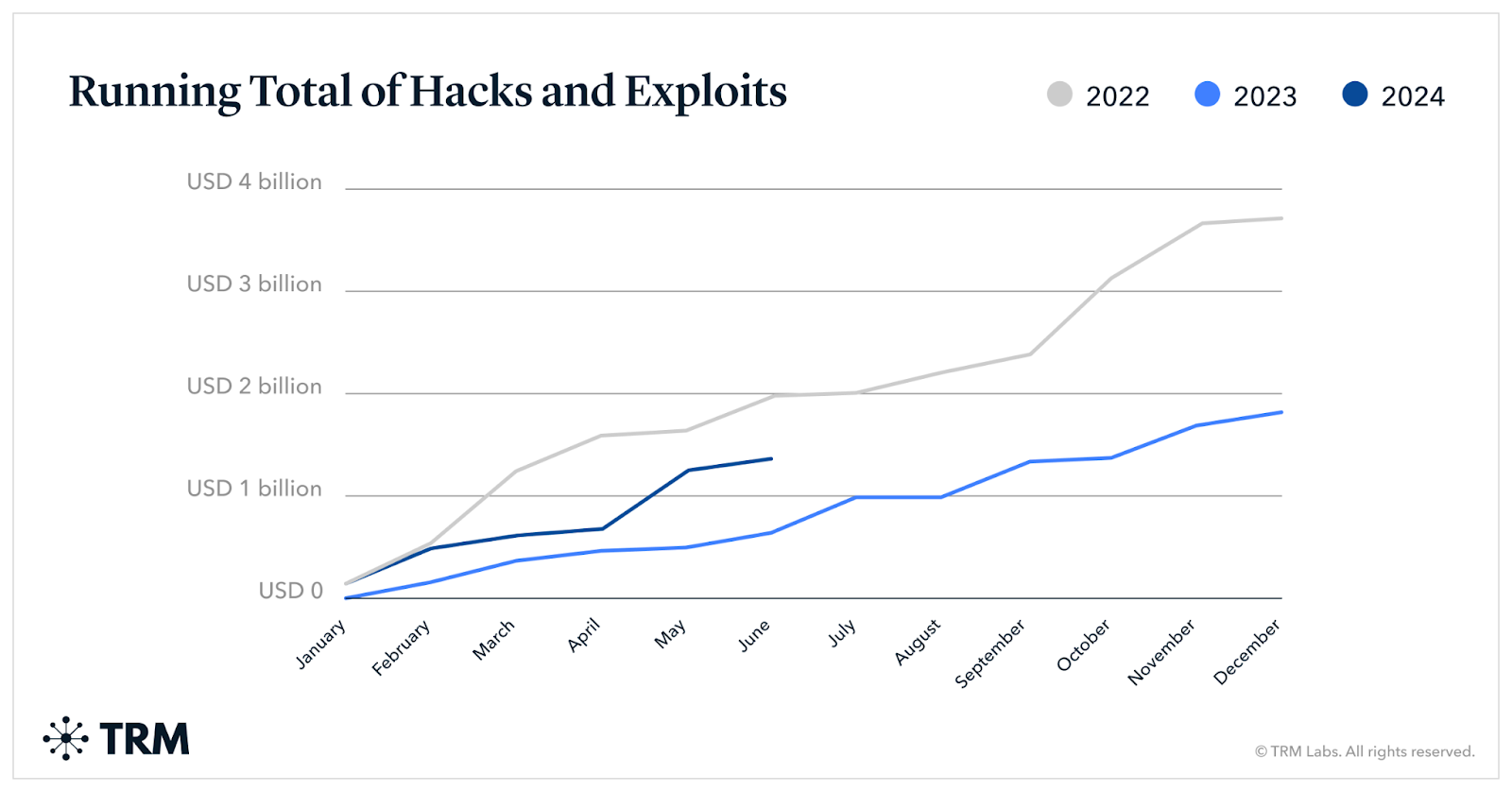
In 2024, crypto theft amounted to $1.38 billion from January 1st to June 24th, according to a report published by TRM Labs. The data suggests, the stolen crypto wealth has doubled in 2024 compared to the $657 million that was stolen in 2023 between the same timeframe. The 2024 crypto loots followed a similar trend to those in 2023, wherein nearly 70% of the stolen wealth was the result of the top 5 hacks.
Japanese cryptocurrency exchange DMM Bitcoin suffered the largest loot in 2024, losing more than 4,500 BTC worth upwards of $300 million. The report’s findings highlight the vulnerability of private keys and address poisoning as notable methods to hack into individual crypto wallets. Through address poisoning, hackers transfer minimal amounts of cryptocurrency to the targeted accounts to forge a transaction history that would prompt users to engage in future transactions with the fraudulent account. A primary tactic used in most cryptocurrency hacks in the past. Aside from address poisoning and compromising private keys, crypto hackers have also exploited seed phrases to perform large-scale hacks.
Interestingly, the TRM Labs reports indicate that between 2023 and 2024, no new vectors have been utilized to organise these elaborate hacks, and “no fundamental changes in the security of the cryptocurrency ecosystem” were identified to explain this upward trend of malicious activity. However, “higher average token prices” in 2024 compared to 2023 may point to a persistent rise in crypto theft.
Creating a robust defense strategy against crypto hacks
The report stresses the urgency of adopting a multiprong approach towards safeguarding crypto projects. This may include regular security audits, robust encryption, multi-signature wallets, and secure coding practices. Additionally, a prompt response strategy is essential to minimizing the impact of these phishing attacks. Offering a handsome bounty in return for the stolen assets has emerged as a popular strategy in recent years. Despite these practices, several experts, including researchers at TRM Labs, advise users to adopt a “defense-in-depth approach, where multiple, redundant security measures are in place to provide the best protection against potential breaches.”






